-
THC Gummies
Delicious THC GummiesTHC Gummies -
THC Hard Candy
Long Lasting Hard CandyTHC Hard Candy -
THC Cereal Bars
Scrumptious THC Cereal BarsTHC Cereal Bars -
THC Lollipops
Succulent SuckersTHC Lollipops -
CBD Products
All Things CBD -
THC / CBD Combo Products
Best Of Both Worlds!
-
THC Gummies
Delicious THC GummiesTHC Gummies -
THC Hard Candy
Long Lasting Hard CandyTHC Hard Candy -
THC Cereal Bars
Scrumptious THC Cereal BarsTHC Cereal Bars -
THC Lollipops
Succulent SuckersTHC Lollipops -
CBD Products
All Things CBD -
THC / CBD Combo Products
Best Of Both Worlds!
THC vs CBD
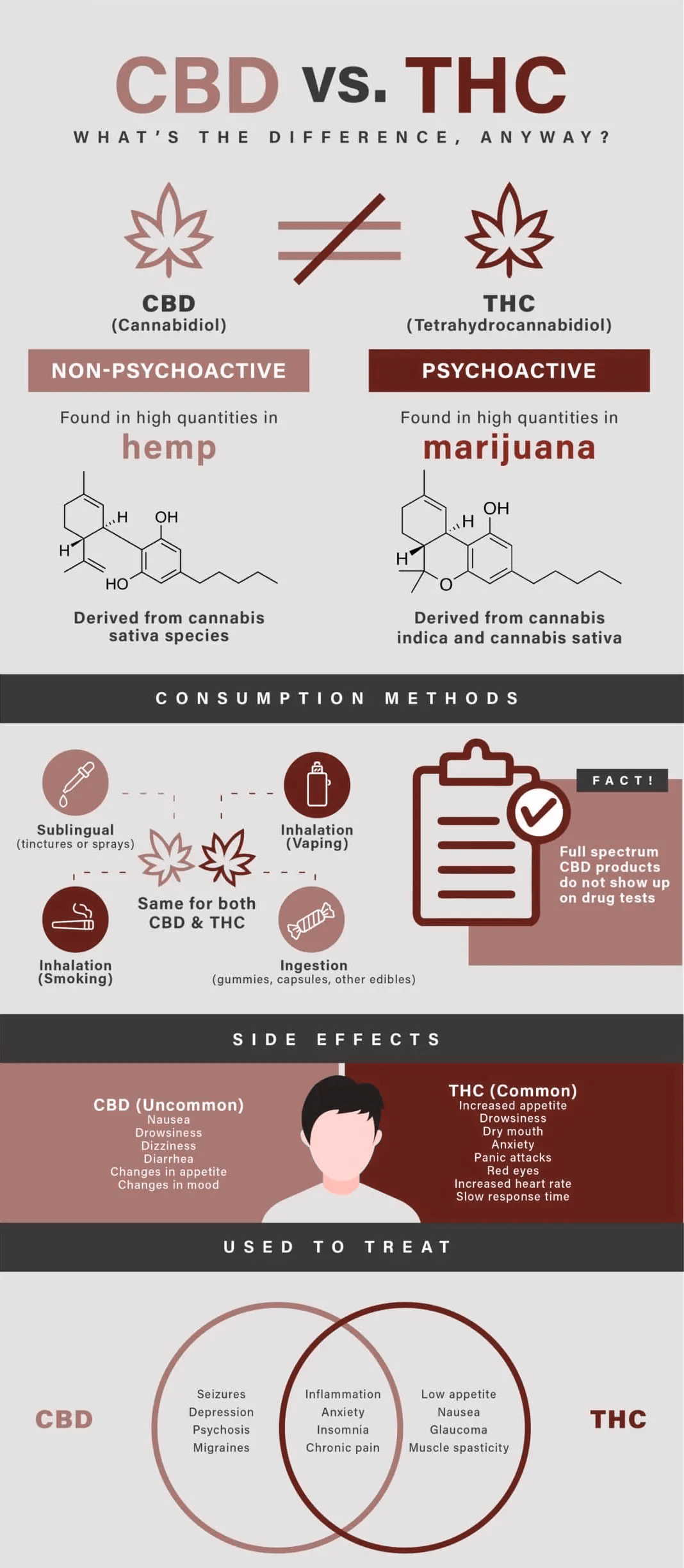
What is the difference between CBD and THC?
The roots of their differences are in the plants themselves. Cannabis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae, which include hemp and marijuana, among other species.
Both hemp and marijuana contain cannabinoids – naturally occurring compounds – and there are at least 144 currently known. Two of the most well known cannabinoids are Cannabidiol (CBD) and Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Hemp and marijuana plants also differ in how they grow, what they look like, and how they are farmed. This also determines their legality in different countries and states in the US. In Canada, products made of industrial hemp are legal. It is also legal to grow hemp with the appropriate licence. Hemp farming is licensed under the Industrial Hemp Program. In Canada, hemp products and marijuana are both regulated under The Cannabis Act (Bill C-45).
CBD vs THC: why one gets you high and the other doesn’t
To break the plant down further, the cannabis genus contains at least three recognizable species: indica, sativa and ruderalis. Industrial hemp falls under the cannabis sativa species. “Industrial hemp” is defined as Cannabis Sativa specifically cultivated for non-drug use — i.e. it contains less than 0.3% THC (more on this later).
The biggest differentiator between hemp and marijuana is their chemical makeup. While marijuana contains high amounts of THC (anywhere between 5-30%), hemp contains no more than 0.3% THC, and comparatively high amounts of CBD.
This distinguishing factor between CBD and THC causes each to interact with the body in different ways – this creates the ultimate discriminator in CBD vs THC: THC gives you a high while CBD does not.
Hemp has no psychoactive components, meaning it contains so little THC that hemp-derived CBD products won’t get high or cause psychoactive impairment of any kind.
The Endocannabinoid System: what is it and how CBD and THC interact with it
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS), acts as the body’s “universal regulator,” according to a 2018 study.
The ECS plays an important role in helping to maintain homeostasis in the body. This homeostasis encompasses the immune system, the brain and endocrine system. The ECS is so impactful in the body, “due to an abundance of cannabinoid receptors located anywhere from immune cells to neurons,” the same study, published in The Journal of Young Investigators, found.
This study also links cannabis to the ECS. It found that the cannabis plant can function as a mass stimulation to the body’s ECS and therefore the body processes these phytocannabinoids (any cannabinoid produced in the trichomes of a cannabis plant) as endocannabinoids.
This is all very scientific speak to basically say CBD and THC naturally interact with the body, but they do so in different ways. THC binds to the ECS and CBD does not. This is why THC gets you high and CBD does not.

THC, CBD, & CB1 receptors
THC interacts or activates the cannabinoid 1 receptors (CB1) in the body’s ECS. CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system. When the CB1 receptors are activated, a psychoactive effect is produced – you get high.
CBD on the other hand, does not bind with CB1 receptors and therefore no psychoactive effects occur. As a phytocannabinoid, CBD stimulates ECS receptor responses that can bring about therapeutic effects to the mind and body.
CBD continues to grow as a natural treatment for common ailments and pain from skin issues, to headaches, anxiety to arthritis. While scientific studies and research on the full effects and benefits of CBD are ongoing, what research has found so far is that CBD’s natural interaction with the body’s ECS can offer an alternative and natural solution to ibuprofen and other synthetic anti-inflammatory medications.
Information provided by https://resolvecbd.co

Do you have any questions?
EddyBull@cbdbros.club

+1 (413) 250-7612
Mon - Fri: 8:00 - 17:00
What you want

Free Shipping & Handling
For all orders over $150

Products Tested In House
For Strength and Quality.

Support 24/7
E-mail and Chat Available





















